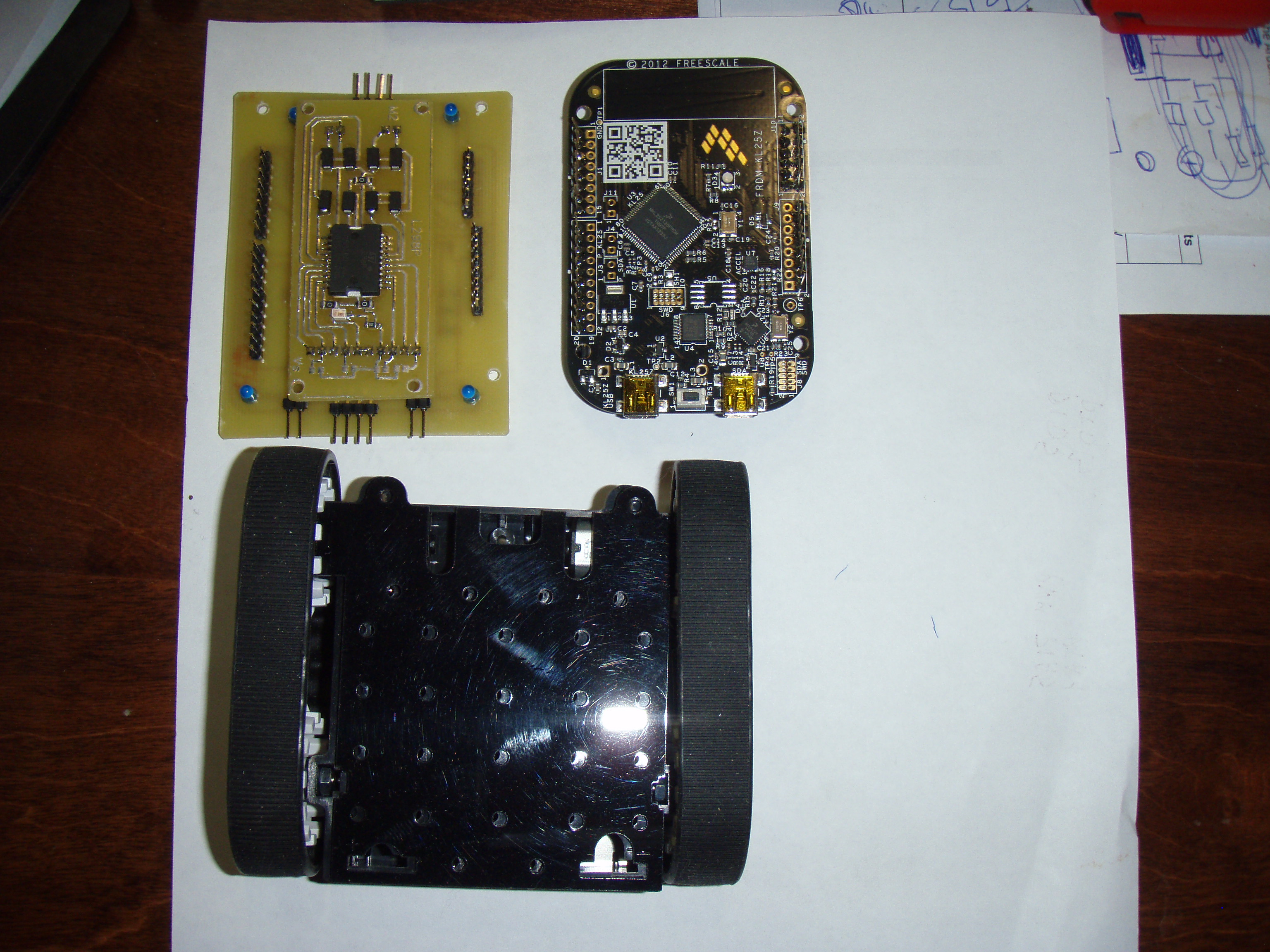
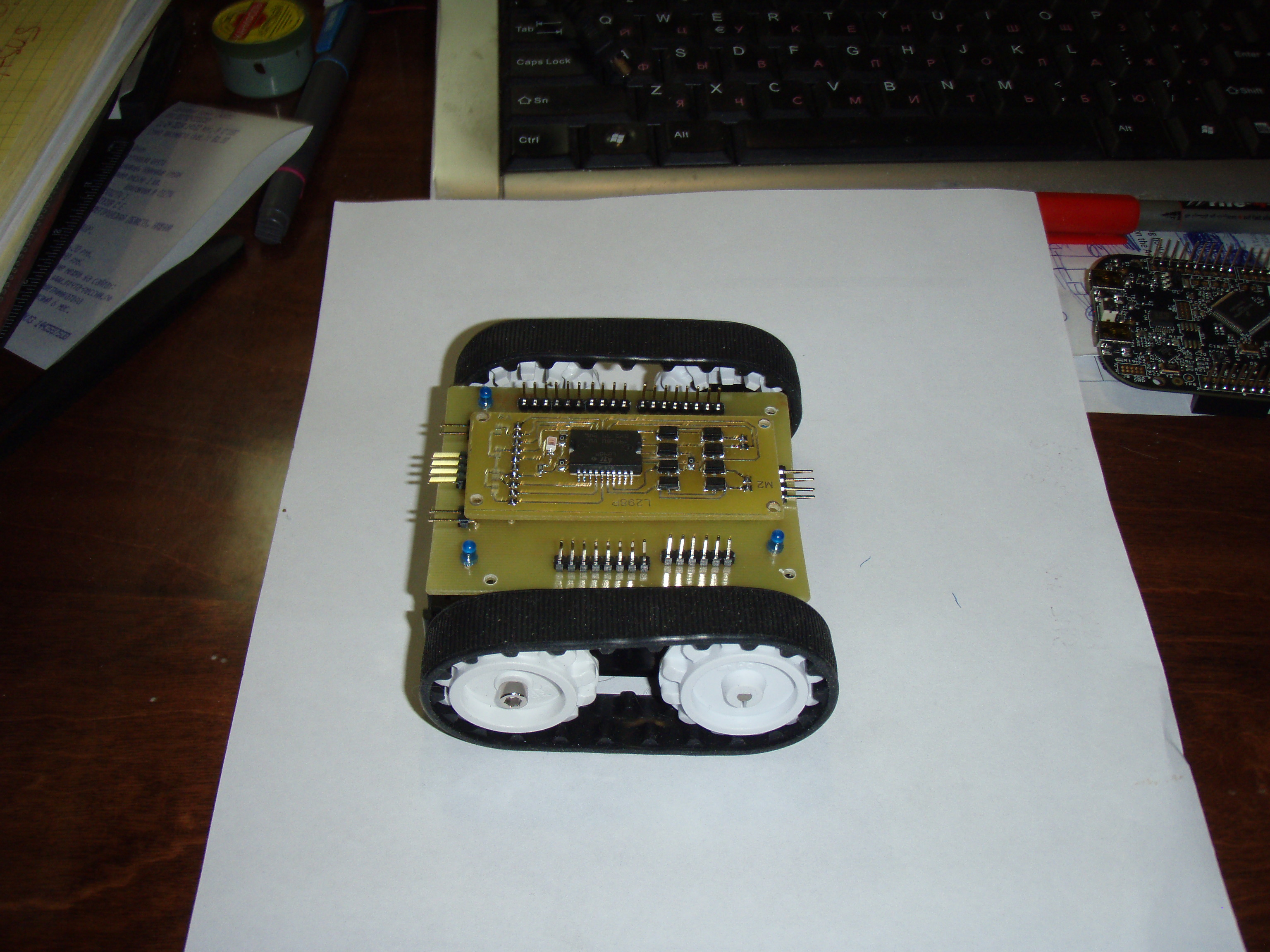
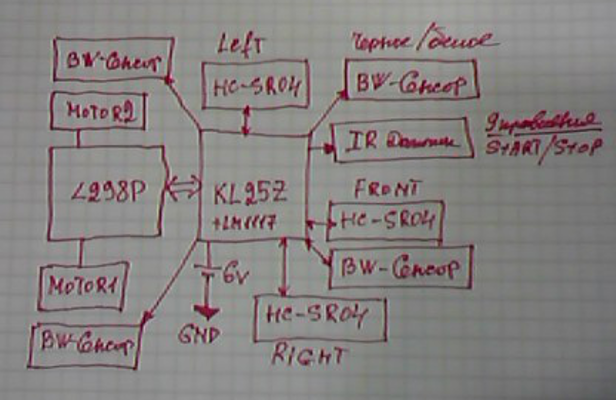
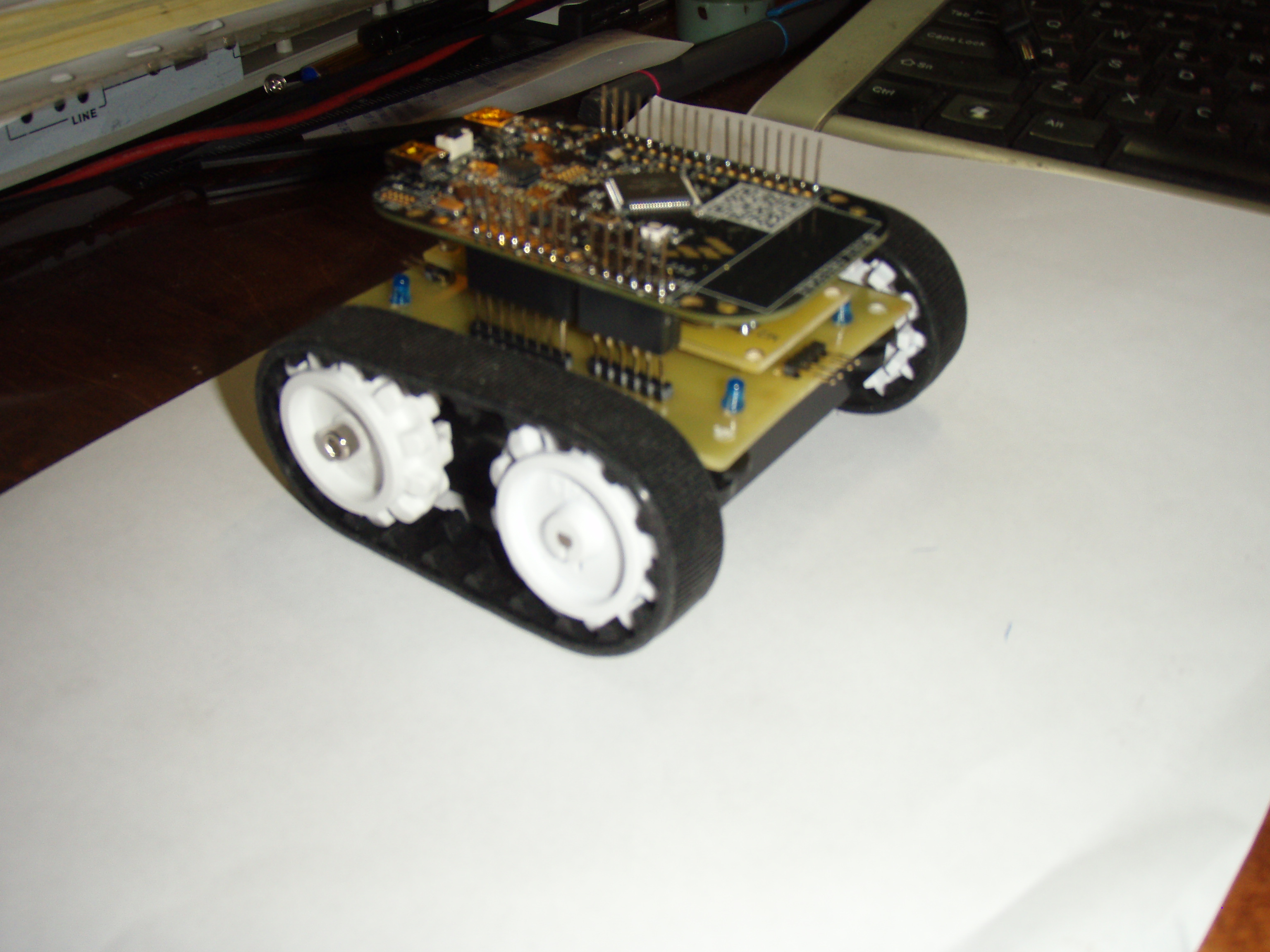
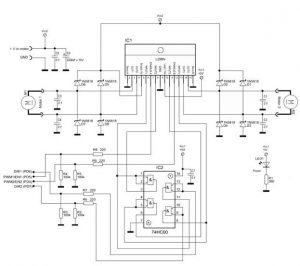
И так начинаем строить робота для соревнований по мини сумо.
Пока только первый этап, это контролер и шасси с двигателями.
Драйвер моторов: Motor Driver 1A Dual TB6612FNG
Контролер: FRDM-KL05Z
Шасси ZUMO.
Вес с батарейками 247 г.
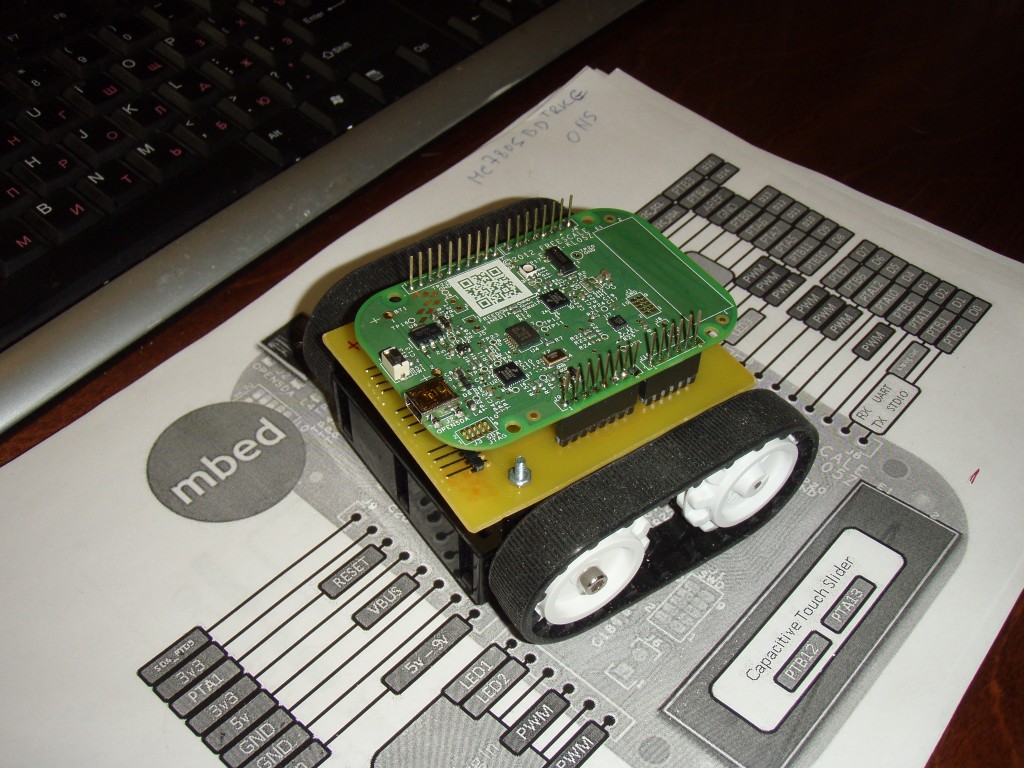

Добавили плату с датчиками:
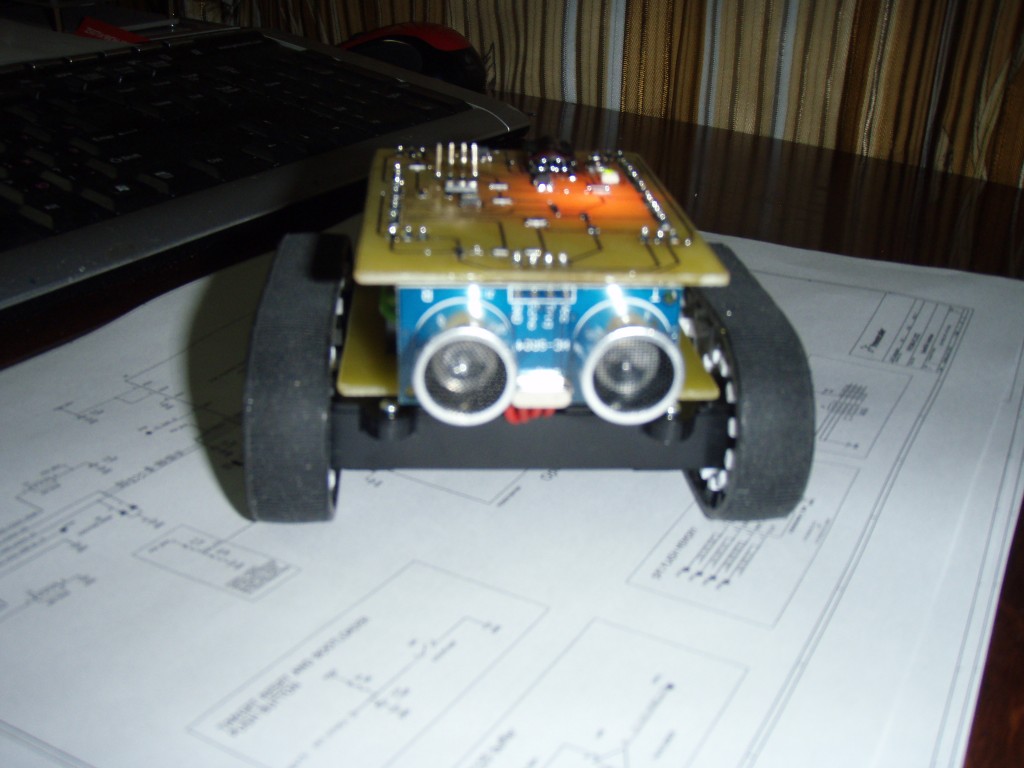


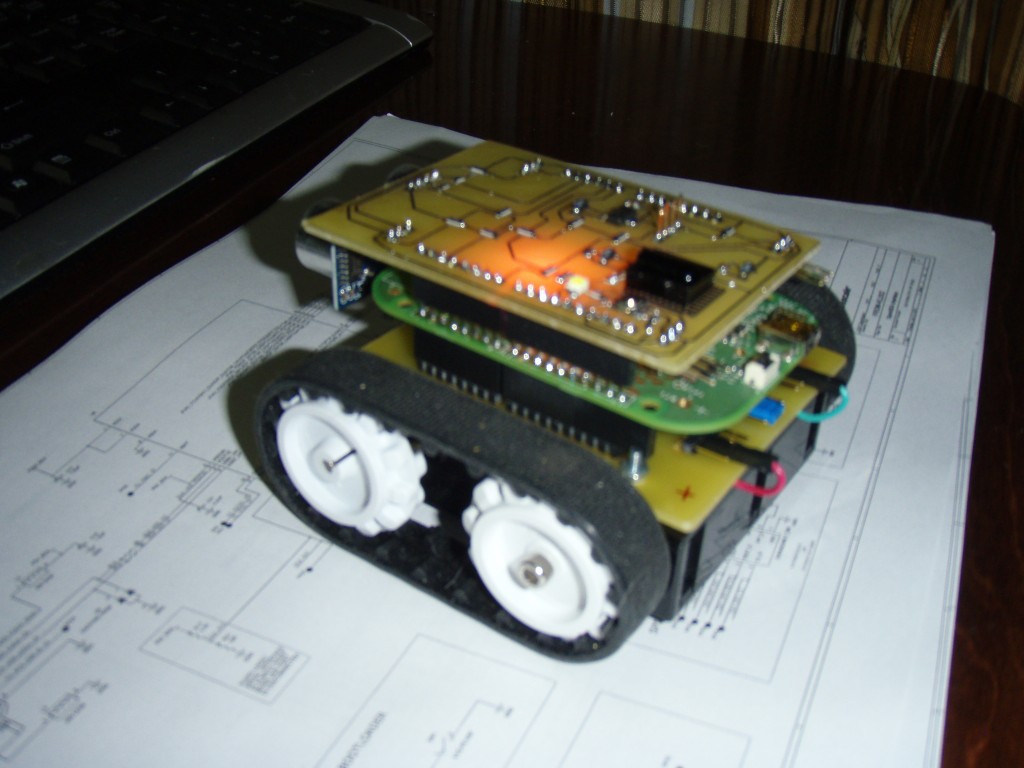

Схема подключения HC-SR04 к FRDM-KL05Z
/* Test */
#include "mbed.h"
#include "ReceiverIR.h"
// PinName const SDA = PTB4;
// PinName const SCL = PTB3;
// --------------- Верхний Уровень -------------------------------
// A5 BW-Sense - FRONT
// A3 BW-Sense - FRONT
// A1 BW-Sense - REAR
// A0 BW-Sense - REAR
float getRange();
void falling(void);
void rising(void);
DigitalOut trig(D2); // Triger for HC-SR04
InterruptIn echo(D0); // D0
Timer tmr;
int delay = 0;
float range = 0.0;
// DigitalIn sStart(D7) // Signal for Start and Running
// DigitalIn IR(D11) // Input from IR Receiver
// DigitalIn But(D13); // Buttom 1-Press (0-Down)
DigitalOut mLED(D12); // LED
ReceiverIR ir_rx(D11);
// --------------- Нижний уровень --------------------------------
// Motor B
PwmOut PWMB(D10); //Speed control
DigitalOut BIN1(D8); //Direction
DigitalOut BIN2(D9); //Direction
DigitalOut STBY(D6) ; //standby
//Motor A
PwmOut PWMA(D3); // Speed control
DigitalOut AIN1(D5); // Direction
DigitalOut AIN2(D4); // Direction
void move(int motor, float speed, int direction);
void stop();
void forward();
void reverse();
void left();
void right();
#define STOP 0
#define FORWARD 1
int COMMAND = STOP;
void rising(void)
{
tmr.reset();
tmr.start();
}
// Stop and read the timer at the end of the pulse
void falling(void)
{
tmr.stop();
delay = tmr.read_us();
}
float getRange()
{
// send a trigger pulse, 20uS long
trig = 1;
// wait (0.000002);
wait_us(10);
trig = 0;
// Timer starts on rising edge of echo
// Timer stopped and read on falling edge
// wait 50ms as a time out (there might be no echos)
wait(0.050);
return delay/58.0;
}
int main(void)
{
STBY = 0; // Моторы Выключены
mLED = 1;
// RemoteIR::Format format;
// int bitcount;
// uint8_t buf[32];
echo.rise(&rising);
echo.fall(&falling);
while (true) {
// if (ir_rx.getState() == ReceiverIR::Received) {
// bitcount = ir_rx.getData(&format, buf, sizeof(buf) * 8);
// for(int i=0; i<sizeof(buf); i++) printf("%0X ",buf[i]);
// printf("\n%d\n",bitcount);
// }
printf("%f\n",getRange()); // Печатать расстояние от HC-SR04
wait(0.5);
mLED = !mLED;
wait(0.5);
}
}
void move(int motor, float speed, int direction)
{
// Move specific motor at speed and direction
// motor: 0 for B 1 for A
// speed: 0 is off, and 255 is full speed
// direction: 0 clockwise, 1 counter-clockwise
STBY = 1; //disable standby
int inPin1 = 1;
int inPin2 = 0;
if(direction == 1) {
inPin1 = 0;
inPin2 = 1;
}
if(motor == 1) {
AIN1 = inPin1;
AIN2 = inPin2;
PWMA = speed;
} else {
BIN1 = inPin1;
BIN2 = inPin2;
PWMB = speed;
}
}
void stop()
{
STBY = 0; // enable standby
AIN1 = 0;
AIN2 = 0;
PWMA = 0.0;
BIN1 = 0;
BIN2 = 0;
PWMB = 0.0;
}
void forward()
{
move(1, 1.0, 0); //motor 1, full speed, left
move(2, 1.0, 1); //motor 2, full speed, left
}
void reverse()
{
move(1, 1.0, 1); //motor 1, full speed, left
move(2, 1.0, 0); //motor 2, full speed, left
}
void left()
{
move(1, 0.5, 1); //motor 1, full speed, left
move(2, 0.5, 1); //motor 2, full speed, left
}
void right()
{
move(1, 0.5, 0); //motor 1, full speed, left
move(2, 0.5, 0); //motor 2, full speed, left
}
Что нужно сделать в другой версии: (To DO)
- Мало индикации
- Мало кнопок управления, все только через IR
- Sharp GP2D12 (от 0 до 130 см)